De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod op moderne markten
De De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod Ze vormen de hoeksteen van de economische theorie en bepalen hoe markten functioneren en prijzen worden vastgesteld.
Anúncios
Dit fundamentele concept verklaart de wisselwerking tussen de beschikbaarheid van goederen of diensten (aanbod) en de behoefte daaraan (vraag).
Het begrijpen van deze dynamiek is cruciaal voor bedrijven, beleidsmakers en consumenten die zich in de complexe wereldmarkten van vandaag de dag moeten begeven.
De eenvoud van het vraag-aanbodmodel verhult echter de diepgaande impact ervan op alles, van lokale supermarkten tot internationale handelsakkoorden.
Anúncios
Hoe beïnvloeden deze krachten de wereld om ons heen, en waarom blijven ze relevant in een tijdperk van digitale economieën en snelle innovatie?
Dit artikel gaat dieper in op de basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod, en onderzoekt de mechanismen, toepassingen in de praktijk en nuances in moderne markten.
Door nieuwe perspectieven, originele voorbeelden en data-gestuurde inzichten met elkaar te verweven, zullen we onthullen hoe deze principes de besluitvorming beïnvloeden en het economische landschap vormgeven.
++ Hoe maak je een eenvoudig en effectief bedrijfsplan?
De kernmechanismen van vraag en aanbod

In essentie is de De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod Het draait om een delicate balans.
Het aanbod vertegenwoordigt de hoeveelheid van een goed of dienst die producenten bereid zijn aan te bieden tegen verschillende prijzen, terwijl de vraag aangeeft hoeveel consumenten bereid zijn te kopen tegen die prijzen.
Het samenspel tussen deze krachten bepaalt bijgevolg de evenwichtsprijs, waar vraag en aanbod op elkaar aansluiten.
++ 7 prijspsychologische trucs die je kunt gebruiken in je kleine onderneming
Als bijvoorbeeld een nieuw smartphonemodel met een hoge prijs op de markt komt, kan de vraag aanvankelijk laag zijn, waardoor fabrikanten de prijzen verlagen totdat de verkoop stijgt.
Neem bijvoorbeeld de markt voor ambachtelijke koffie in een kleine stad.
De lokale koffiebranderij JavaJoy produceert maandelijks 1.000 zakken speciale koffie. Met een prijs van $20 per zak zijn deze door de grote vraag van koffieliefhebbers snel uitverkocht.
Als JavaJoy de prijs echter verhoogt naar $30, daalt de vraag, waardoor er onverkochte voorraad overblijft.
Dit scenario illustreert hoe prijsaanpassingen vraag en aanbod op elkaar afstemmen en zo de marktstabiliteit waarborgen.
Bovendien kunnen externe factoren, zoals consumentenvoorkeuren of productiekosten, deze curves verschuiven en nieuwe evenwichtspunten creëren.
De schoonheid van dit model schuilt in zijn aanpasbaarheid. In tegenstelling tot rigide economische theorieën reageren vraag en aanbod dynamisch op veranderingen in de praktijk.
Tijdens een droogteperiode kan de koffieproductie bijvoorbeeld drastisch dalen, waardoor het aanbod afneemt en de prijzen stijgen.
Omgekeerd kan een virale trend op sociale media de vraag naar een specifieke melange juist doen toenemen, waardoor koffiebranders gedwongen worden de productie op te schalen.
Het begrijpen van deze mechanismen stelt bedrijven in staat om marktverschuivingen te anticiperen en weloverwogen beslissingen te nemen.
| Factor | Impact op het aanbod | Impact op de vraag |
|---|---|---|
| Prijsverhoging | Stimuleert meer productie | Vermindert de gevraagde hoeveelheid |
| Productiekosten | Hogere kosten leiden tot een afname van het aanbod. | Geen direct effect |
| Consumententrends | Geen direct effect | De vraag verschuift op basis van populariteit. |
| Externe schokken | Verstoring van de toevoer (bijv. natuurrampen) | Kan de vraag beïnvloeden (bijvoorbeeld door paniekaankopen). |
Vraag en aanbod op moderne markten

Moderne markten voegen extra complexiteit toe aan de De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbodGlobalisering, technologie en consumentengedrag hebben de manier waarop deze krachten op elkaar inwerken, veranderd.
++ Wat ondernemers kunnen leren van straatverkopers
E-commerceplatforms zoals Amazon maken bijvoorbeeld directe prijsaanpassingen mogelijk op basis van realtime vraaggegevens, iets wat heel anders is dan bij traditionele fysieke winkels.
Hierdoor kunnen bedrijven snel reageren op marktsignalen en hun prijsstrategieën optimaliseren om de winst te maximaliseren.
Neem bijvoorbeeld FitPulse, een fitness-app op abonnementsbasis.
Wanneer FitPulse zijn maandelijkse kosten verlaagt van $15 naar $10, stijgt het aantal abonnementen met 40%, wat wijst op een toegenomen vraag.
Als de serverkosten echter stijgen als gevolg van toegenomen gebruikersactiviteit, kan FitPulse genoodzaakt zijn om gratis functies te schrappen, waardoor het aanbod effectief afneemt.
Deze wisselwerking benadrukt hoe digitale markten de snelheid en schaal van aanpassingen in vraag en aanbod versterken.
Bovendien stelt data-analyse bedrijven in staat om vraagtrends te voorspellen, waardoor proactieve in plaats van reactieve strategieën mogelijk worden.
Ook wereldwijde toeleveringsketens geven deze dynamiek een nieuwe vorm.
Neem bijvoorbeeld het tekort aan halfgeleiders in 2021-2023, dat de levering van elektronica zoals spelconsoles beperkte.
Volgens Statista daalde de wereldwijde verkoop van halfgeleiders in 2022 met 7,31 TP3T als gevolg van verstoringen in de toeleveringsketen, waardoor de prijzen stegen omdat de vraag het aanbod overtrof.
Dit voorbeeld onderstreept hoe onderling verbonden markten de domino-effecten van aanbodbeperkingen versterken, waardoor bedrijven worden uitgedaagd zich snel aan te passen.
De rol van externe invloeden
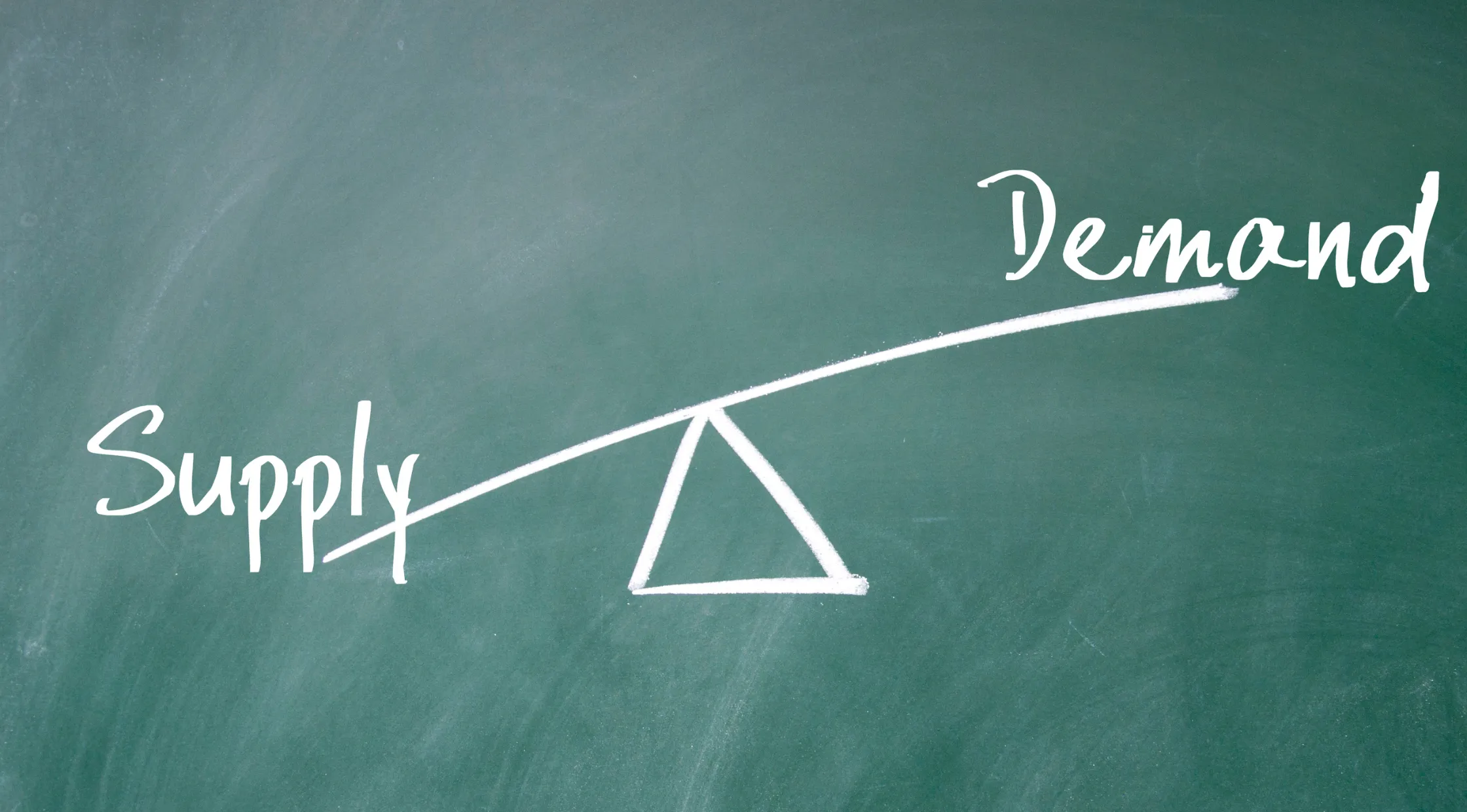
Externe factoren verstoren vaak de De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbodwaardoor onvoorspelbaarheid ontstaat.
Overheidsbeleid, zoals tarieven of subsidies, kan de kosten van de toelevering of de koopkracht van de consument beïnvloeden.
Een subsidie voor elektrische voertuigen (EV's) stimuleert bijvoorbeeld de vraag door de effectieve kosten voor kopers te verlagen, terwijl invoerrechten op batterijen het aanbod kunnen beperken en de prijzen kunnen verhogen.
Beleidsmakers moeten daarom interventies zorgvuldig afstemmen om onbedoelde marktverstoringen te voorkomen.
Een analogie helpt deze complexiteit te verduidelijken: zie vraag en aanbod als een wip. Wanneer ze in evenwicht zijn, draait de markt soepel.
Externe factoren, zoals een plotselinge wetswijziging of een natuurramp, kunnen echter de doorslag geven aan één kant en het evenwicht verstoren.
Bedrijven en consumenten moeten zich vervolgens aanpassen om het evenwicht te herstellen.
Deze dynamische aard maakt de De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod Het is zowel een wetenschap als een kunst, die scherpe observatie en aanpassingsvermogen vereist.
Bovendien speelt consumentenpsychologie een cruciale rol.
Tijdens de pandemie van 2020 zorgde de paniek rond de aankoop van toiletpapier voor een enorme stijging van de vraag, ondanks stabiele toeleveringsketens.
Winkeliers hadden moeite om hun schappen gevuld te houden, wat illustreert hoe perceptie rationeel marktgedrag kan overschrijven.
Waarom laten we ons soms door angst of hype leiden bij onze economische beslissingen?
Het begrijpen van deze psychologische triggers is net zo belangrijk als het beheersen van de technische aspecten van vraag en aanbod.
| Externe invloed | Effect op het aanbod | Effect op de vraag |
|---|---|---|
| Overheidssubsidies | Verhoogt het aanbod (lagere productiekosten) | Stimuleert de vraag (lagere consumentenprijzen) |
| Tarieven/Handelsbelemmeringen | Vermindert het aanbod (hogere importkosten) | Kan de vraag verminderen (hogere prijzen) |
| Consumentenvertrouwen | Geen direct effect | Verschuivingen in de vraag (bijv. paniekaankopen) |
| Technologische vooruitgang | Verhoogt het aanbod (efficiëntiewinst) | Kan de vraag stimuleren (nieuwe productkenmerken) |
Praktische toepassingen en uitdagingen
Het toepassen van de De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod In de praktijk brengt dit unieke uitdagingen met zich mee. Neem bijvoorbeeld de woningmarkt in stedelijke gebieden.
In steden als San Francisco botst het beperkte aanbod aan grond met de torenhoge vraag, waardoor de gemiddelde huizenprijzen volgens gegevens van Zillow in 2024 oplopen tot 1,4 miljoen dollar.
Ontwikkelaars worden geconfronteerd met bestemmingsplanbeperkingen, die het aanbod beperken, terwijl goedbetaalde banen in de technologiesector de vraag aanwakkeren.
Daardoor blijft een evenwicht moeilijk te bereiken, waardoor veel kopers worden buitengesloten vanwege de hoge prijzen.
Een ander voorbeeld is de opkomst van plantaardige vleesvervangers.
Beyond Meat, een toonaangevend merk, kreeg aanvankelijk te maken met een overweldigende vraag toen consumenten steeds vaker kozen voor een duurzaam voedingspatroon.
Het opschalen van de productie om aan deze vraag te voldoen bleek echter een uitdaging vanwege de complexe toeleveringsketens voor erwteneiwit en andere ingrediënten.
Daardoor bleven de prijzen hoog, wat de groei van de vraag temperde.
Deze casus illustreert hoe aanbodbeperkingen de marktuitbreiding kunnen belemmeren, zelfs wanneer de vraag groot is.
Uitdagingen ontstaan ook door informatieasymmetrie.
Consumenten hebben mogelijk onvoldoende inzicht in de waarde van een product, waardoor de vraag vertekend raakt, terwijl producenten de marktbehoeften verkeerd kunnen inschatten en daardoor te veel of te weinig goederen aanbieden.
Het benutten van data-analyse en marktonderzoek is daarom essentieel voor een effectieve afstemming van vraag en aanbod.
Bedrijven die deze afstemming beheersen, verkrijgen een concurrentievoordeel in dynamische markten.
Veelvoorkomende misvattingen en verduidelijkingen
Misverstanden over de De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod kan leiden tot gebrekkige beslissingen.
Een veelvoorkomende misvatting is dat prijzen altijd de kwaliteit weerspiegelen. In werkelijkheid worden prijzen vooral bepaald door de dynamiek van vraag en aanbod, niet door de intrinsieke waarde.
Luxeartikelen hebben bijvoorbeeld vaak hoge prijzen vanwege het kunstmatig beperkte aanbod, en niet vanwege superieur vakmanschap.
Het herkennen van dit onderscheid helpt consumenten om weloverwogen keuzes te maken.
Een andere misvatting is dat vraag en aanbod los van elkaar functioneren. In werkelijkheid staan ze in wisselwerking met talloze variabelen, van culturele trends tot technologische veranderingen.
Zo heeft de opkomst van thuiswerken bijvoorbeeld de vraag naar kantoorruimte doen afnemen, terwijl de vraag naar apparatuur voor thuiswerken juist is toegenomen.
Bedrijven moeten daarom rekening houden met de bredere marktcontext om veranderingen nauwkeurig te kunnen voorspellen.
Tot slot gaan sommigen ervan uit dat markten altijd vanzelf een evenwicht bereiken.
Externe schokken of structurele belemmeringen, zoals monopolies, kunnen dit evenwicht echter verstoren.
Beleidsmakers en bedrijven moeten deze factoren actief in de gaten houden om gezonde markten te bevorderen.
Door deze mythen te ontkrachten, krijgen we een helderder beeld van de economische dynamiek.
De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod: veelgestelde vragen
| Vraag | Antwoord |
|---|---|
| Wat veroorzaakt veranderingen in het aanbod? | Het aanbod verschuift als gevolg van productiekosten, technologie, regelgeving of externe schokken zoals natuurrampen. |
| Hoe beïnvloedt de vraag de prijzen? | Een hogere vraag leidt doorgaans tot hogere prijzen, terwijl een lagere vraag juist tot prijsverlagingen kan leiden. |
| Zijn vraag en aanbod ook van toepassing op diensten? | Ja, diensten zoals streaming of consultancy volgen dezelfde principes: het afwegen van beschikbaarheid en de belangen van de consument. |
| Waarom bereiken markten niet altijd een evenwicht? | Externe factoren zoals regelgeving, monopolies of plotselinge verstoringen kunnen het evenwicht verstoren. |
| Hoe beïnvloeden mondiale gebeurtenissen vraag en aanbod? | Gebeurtenissen zoals pandemieën of handelsoorlogen kunnen het aanbod beperken of de vraag veranderen, wat prijsvolatiliteit veroorzaakt. |
Conclusie: de basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod
De De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod blijven een krachtig instrument om moderne markten te begrijpen.
Van lokale bedrijven tot wereldwijde industrieën: deze principes vormen de leidraad voor prijsbepaling, productie en consumentengedrag.
Door praktijkvoorbeelden te onderzoeken, zoals ambachtelijke koffie en plantaardig vlees, zien we hoe vraag en aanbod zich aanpassen aan hedendaagse uitdagingen.
Bovendien voegen externe invloeden zoals overheidsbeleid, consumentenpsychologie en mondiale gebeurtenissen extra complexiteit toe, waardoor genuanceerde strategieën nodig zijn om hiermee om te gaan.
Naarmate markten zich ontwikkelen, wordt het beheersen van deze basisprincipes steeds belangrijker.
Bedrijven die data benutten, veranderingen anticiperen en externe verstoringen aanpakken, zullen floreren in dit dynamische landschap.
Voor consumenten betekent inzicht in deze krachten dat ze betere beslissingen kunnen nemen.
Uiteindelijk, de De basisprincipes van vraag en aanbod Het zijn niet zomaar economische theorieën; ze vormen de hartslag van de markten, bruisend van kansen en uitdagingen.
